Clear disk
Author: s | 2025-04-25
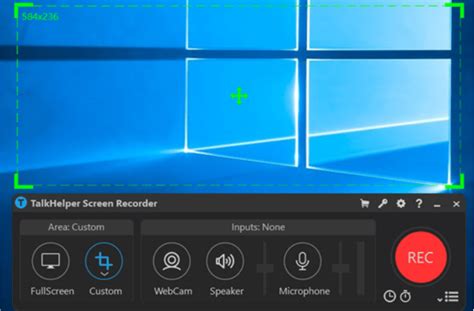
Clear Disk - The disk is cleared and the Unraid signature is written to the disk. This will create an empty partition on the disk. Erase Disk - Erase the entire disk by writing all
Clear Disk - Free up Disk Space
Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes“When store files to my external hard drive, I get an error message says it is write-protected and I cannot write any data to the disk. Then I Google the message and was told to solve the problem with Diskpart. Here are the command lines: list disk > select disk 2 > attributes disk clear readonly. And then I get the prompting says: Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes. Well, guess I’ve got another problem. Any suggestion will be appreciated.”Did you come across the same problem? Search on the Internet, you can find Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes error also happens on USB flash drive, SD card, Pen drive, even internal hard drive in Windows 7, 8, 10, 11, XP and even Windows Server 2008/2012.Disk attributes refer to disk characteristics such as disk free (MB), disk name, disk used (MB), file system status, file system type, inodes free and inodes used. Essentially, the disk attributes readonly refers to write-protected issue, i.e. you cannot write and modify any data on that volume or disk. Due to some kinds of reasons, Diskpart cannot remove the read only cluster successfully. What will be illustrated in this post is why you get the failed error message and how to remove the read only disk attributes in other methods.Why Diskpart failed to clear disk read only cluster?Every problem has its causes. If you find Diskpart failed to remove the read only attributes, it could be explained by one of Clear Disk - The disk is cleared and the Unraid signature is written to the disk. This will create an empty partition on the disk. Erase Disk - Erase the entire disk by writing all Clear Disk - The disk is cleared and the Unraid signature is written to the disk. This will create an empty partition on the disk. Erase Disk - Erase the entire disk by writing all The power supply reading values displayed in Watts. Status The power status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Voltages Sensor Name of the voltage supply. Reading (Volts) The voltage reading values displayed in Volts. Status The voltage status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Battery Sensor Name of the Battery sensor. Status The battery status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Memory Sensor Name of the Memory sensor. Memory Device Type The type of memory device. Size (MB) The amount of memory currently installed in MB. Status The memory status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Disk Sensor Identifies the disk's label. Device Name The device name configured for the disk. Size (MB) The allocated size in MB. Status The disk status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Array Sensor The name of the array disk. Bus protocol The bus type of the array disk. Size (MB) The amount in MB of the used space on the array disk. Status The array status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Chassis Sensor The user-assigned chassis name of the chassis. Model The system model type for this chassis. Status The chassis status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Processor Sensor The location name of the processor device status probe. Processor Brand The brand of the processor device. Processor Current Speed The current speed of the processor device in MHz. Processor Core Count The number of processor cores detected for the processor device. Status The processor status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. If a component is functioning normally, the status indicator is green. The status indicator changes to orange or red if a system component violates a performance threshold or is not functioning properly. Generally, an orange indicator signifies degraded performance. A red indicator signifies that a component stopped operating or exceeded the highest threshold. If the status is blank, then the health monitoring service cannot determine the status of the component. -->Note:Currently, hardware performance monitoring is supported in SNMP and WMI monitoring mode.-->Hardware Device-Level ConfigurationHardware Configuration option available under Host Details on the right-hand side of the details page will allow you to opt for the various hardware components you want to monitor. This operation can also be done using the Performance Polling option under the Settings tab which will globally configure the hardware stats.Advanced SettingsBy clicking the Advanced Settings option available under Host Details on the right-hand side of the details page, you can go to the PerformanceComments
Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes“When store files to my external hard drive, I get an error message says it is write-protected and I cannot write any data to the disk. Then I Google the message and was told to solve the problem with Diskpart. Here are the command lines: list disk > select disk 2 > attributes disk clear readonly. And then I get the prompting says: Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes. Well, guess I’ve got another problem. Any suggestion will be appreciated.”Did you come across the same problem? Search on the Internet, you can find Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes error also happens on USB flash drive, SD card, Pen drive, even internal hard drive in Windows 7, 8, 10, 11, XP and even Windows Server 2008/2012.Disk attributes refer to disk characteristics such as disk free (MB), disk name, disk used (MB), file system status, file system type, inodes free and inodes used. Essentially, the disk attributes readonly refers to write-protected issue, i.e. you cannot write and modify any data on that volume or disk. Due to some kinds of reasons, Diskpart cannot remove the read only cluster successfully. What will be illustrated in this post is why you get the failed error message and how to remove the read only disk attributes in other methods.Why Diskpart failed to clear disk read only cluster?Every problem has its causes. If you find Diskpart failed to remove the read only attributes, it could be explained by one of
2025-03-31The power supply reading values displayed in Watts. Status The power status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Voltages Sensor Name of the voltage supply. Reading (Volts) The voltage reading values displayed in Volts. Status The voltage status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Battery Sensor Name of the Battery sensor. Status The battery status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Memory Sensor Name of the Memory sensor. Memory Device Type The type of memory device. Size (MB) The amount of memory currently installed in MB. Status The memory status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Disk Sensor Identifies the disk's label. Device Name The device name configured for the disk. Size (MB) The allocated size in MB. Status The disk status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Array Sensor The name of the array disk. Bus protocol The bus type of the array disk. Size (MB) The amount in MB of the used space on the array disk. Status The array status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Chassis Sensor The user-assigned chassis name of the chassis. Model The system model type for this chassis. Status The chassis status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. Processor Sensor The location name of the processor device status probe. Processor Brand The brand of the processor device. Processor Current Speed The current speed of the processor device in MHz. Processor Core Count The number of processor cores detected for the processor device. Status The processor status - Critical, Warning, and Clear. If a component is functioning normally, the status indicator is green. The status indicator changes to orange or red if a system component violates a performance threshold or is not functioning properly. Generally, an orange indicator signifies degraded performance. A red indicator signifies that a component stopped operating or exceeded the highest threshold. If the status is blank, then the health monitoring service cannot determine the status of the component. -->Note:Currently, hardware performance monitoring is supported in SNMP and WMI monitoring mode.-->Hardware Device-Level ConfigurationHardware Configuration option available under Host Details on the right-hand side of the details page will allow you to opt for the various hardware components you want to monitor. This operation can also be done using the Performance Polling option under the Settings tab which will globally configure the hardware stats.Advanced SettingsBy clicking the Advanced Settings option available under Host Details on the right-hand side of the details page, you can go to the Performance
2025-03-31ModelMore ways to clear storage on Windows 11If you’re looking to reclaim your storage space then there are tons of more things that you can do besides clearing or moving your largest files. You can clear caches, stop programs, reduce dedicated storage space, clear temporary files, remove leftover files, and much more. Refer to this dedicated guide by us that should help you clear space on Windows 11 in every way possible. Should you use disk space analyzers?Disk Space Analyzers have long been the ultimate utility to identify where exactly your disk space is being used. Most of them stem from long-standing communities while others have over decades of experience. If you’re divided on using disk space analyzers, then your best bet would be to opt for something that is open source.The modern world of the internet is centered around data collection and like it or not, every service is gathering and collecting some type of data from your usage of their tool. Hence most disk analyzers nowadays, also have the option to share your usage data and more. Additionally, if you decide to opt for something new and untested then the risks are even higher.Hence, we recommend you use disk space analyzers but do verify their origin and reputation before running them on your system. If you do not wish to go through the hassle of reading reviews, we recommend you simply try an open-source alternative from a trusted source. We hope this guide helped you easily find the largest files using disk space on your system. If you face any issues or errors during the process, feel free to reach out to us using the comments section below.
2025-04-20From this MiniTool article, you can know what the startup disk on your Mac is, what is taking up space on the Mac startup disk, the influence of startup disk full, and how to clear the startup disk space when the startup disk is full or your disk is almost full on your Mac.On This Page :What Is Startup Disk on Mac?What Is Taking Up Space on Your Mac Startup Disk?What Does It Mean When Your Startup Disk Is Full?How to Clear the startup Disk?How to Free up Disk Space on Your Mac?If You Delete Some Important Files on Your Mac by MistakeBottom LineStartup Disk Full FAQWhat Is Startup Disk on Mac?Like a Windows startup disk, the startup disk on your Mac is the disk that saved the operating system on your Mac. It is an important disk on your computer. If the operating system on the disk is corrupted or even the startup disk is damaged, your Mac computer will not boot normally.What Is Taking Up Space on Your Mac Startup Disk?As you know, a Mac computer’s disk is usually not as large as a Windows computer’s disk. As of 2020, Apple has improved the disk capacity and the maximum disk size can reach up to 8TB. But they are the Pro series, which are not widely used.Most of the time, you should not worry about the disk space issue because macOS always do work online. This will not take up much disk space. However, what’s going on if you see a pop-up alert saying Your startup disk is almost full?At this time, you should know what is taking up space on the startup disk of your Mac and then take some measures to clear the startup disk.The hidden website cache takes much space on the startup disk. For example, statistics show that Google Chrome can create numerous cache folders after you visit some web sites. The size of the cache for one site can even reach up to 9 GB. This is quite surprising, but it is true.As time goes on, the free space on the startup disk becomes less and less. One day, you may receive the startup disk full alert.Besides, when a warning of Your disk is almost full pops up, it also means that there is not enough space on your Mac. It is equal to startup disk full. Likewise, you need to remove some files to free up disk space on your Mac computer.What Does It Mean When Your Startup Disk Is Full?When does it mean when you receive your startup disk is almost full alert?It has two main influences:1. You will soon run out of space on the startup disk.Your startup disk is
2025-04-17Data from 1 to 0 (positive to negative).Write data to the external drive. Or, run attributes disk clear readonly again and then write data to that disk. However, if the reason of diskpart failed is not write protected key, you’ll need other solutions.Clear attributes on new RAW USB driveIn some cases, a new USB drive with RAW format can also get readonly error and the error cannot be removed by Diskpart. As covered, it may be affected by inappropriate partition format. In that case, you need to reformat the drive with another file system that can be recognized by Windows. Follow these steps to solve Diskpart failed to clear disk attributes on USB drive.1. Open Run as instructed. Type diskpart and click OK. Run as administrator.2. Type following commands in turn to format RAW drive.• list volume • select volume n (where n is the RAW drive) • format fs=fat32 quick (you can replace “fat32” with “ntfs” or “exfat” as well) • exitNote: You can type attributes disk to see the status of the selected disk.It will be formatted and be recognized by Windows. Now, you can try the disk attributes clear command, or write data to the drive directly if you can. However, if you cannot format RAW drive in Diskpart, please refer to format RAW file system pen drive.Check hard drive for errorsAs mentioned before, bad sectors, partition set hidden and nodefaultdriveletter on the disk are also affecting factors. Therefore, you can check bad sectors to exclude the
2025-04-05Write-protected” message:Run the following diskpart commands: LIST DISKSELECT DISK 2Replace 2 with your disk number2. Finally, to remove the “read-only” attribute, enter this command and press the enter key. ATTRIBUTES DISK CLEAR READONLYSo far, I have discussed how you can use the ATTRIBUTES command to remove the read-only attribute. However, there are instances when you may want to apply the read-only attribute to a disk.One reason you may want to do this is to prevent formatting the disk accidentally. If you want to apply the read-only attribute, use the command below:Before running the command below, run the LIST DISK and SELECT DISK commands. ATTRIBUTES DISK SET READONLYOnce you execute this command on a disk, the disk will “lock” and cannot be formatted. To be able to format the drive, you MUST run the ATTRIBUTES DISK CLEAR READONLY command. How to Use the SHRINK and EXTEND CommandsThe SHRINK command is used to free up unallocated space from a volume or partition. One instance you may need to do this is to create a free space to install a dual-boot Operating System.For instance, you can dual-boot Windows 7 with your existing Windows 10. Furthermore, you may also dual-boot Ubuntu with Windows 10. To use the shrink command to free-up some spaces, run the following commands:LIST DISKSELECT DISK 2Replace 2 with your disk numberLIST PARTITIONSELECT PARTITION 1Replace 1 with your partition number. Finally, use the command below to shrink the partition. Specify the DESIRED and MINIMUM values in MB. SHRINK DESIRED=30000 MINIMUM=10000Alternatively, to
2025-04-11